Poophoria Probiotic
Relieves constipation fast so you get a daily poo-gasm.
Poophoria Probiotic
Relieves constipation fast so you get a daily poo-gasm.

Patented probiotic that survives stomach acid

Gentle relief without cramping or urgency

Reduces pelvic pressure from straining
Most Popular
1 Bottle
1 month supply

3 Bottles
3 months supply

6 Bottles
6 months supply


60-Day Money-Back Guarantee


Expert-Formulated
Additional taxes can be applied. Customers will be responsible for paying duties and taxes upon receipt.
Other women also bought:

Pelvic Bundle
Total relief from bloating, dryness, and fatigue — in one daily ritual.

Buff+
Build strength. Stop leaks. Support your pelvic floor.

Omega Muff
Hydrate from within to end irritation and painful intimacy.

Ships in 24 Hours





Ships in 24 Hours




Tired of feeling backed up and bloated every day?
For women with chronic constipation, bloating, or pelvic issues from straining—fiber isn’t enough. Your gut just needs the right kind of support.

Chronic constipation that won't quit

Bloating and digestive discomfort
Painful straining that weakens your pelvic floor
The cycle of irregular, incomplete bowel movements
You don't need to "just eat more fiber." Your gut just needs the right kind of help.
Four powerhouse ingredients that tackle constipation at the source

LactoWise Probiotic



Turmeric Extract
When To Take These Capsules For Daily Relief

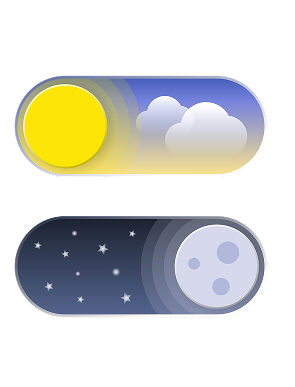
Morning or night, with or without food

No special timing or prep required


Stop falling for probiotic marketing hype

Other Probiotics

50+ billion CFUs that die before reaching your gut




Poophoria

Patented probiotic blend that survives stomach acid

Lower CFU count that actually gets absorbed

Specifically targets gut-pelvic health connection

Clean formula, no artificial fillers or additives
Most women notice

Week 1
Less bloating, easier elimination


"I was chronically constipated my whole life... I poop daily now"
12,000+ women have regained control of their life.
Recommended add-ons

Pelvic Synergy Bundle
Get all 3 products and save 10% off for the bundle, and 15% for the subscription
Shop The Synergy Bundle

Omega Muff
Hydrates from within to relieve vaginal dryness, irritation, and pain.
Shop Omega Muff

Still have questions? We've got answers
How long before it works?
Most women notice easier elimination within 3-7 days, with full benefits developing over 2-4 weeks of consistent use.
Is it safe with my other supplements?
Yes, Poophoria uses natural ingredients that are generally well-tolerated. Always consult your healthcare provider if you have concerns about interactions.
Can I take it long-term?
Absolutely. This gentle formula is designed for ongoing daily use to maintain healthy digestion and pelvic support.
Will it help with bloating or gas too?
Yes, by restoring healthy gut bacteria and improving elimination, most women see significant reduction in bloating and gas.
How many servings in a bottle?
Each bottle contains 60 capsules, providing 30 days of daily use (2 capsules per day).
How long does the product last?
Unopened bottles have a 2-year shelf life. Once opened, use within 6 months for best potency.
How and when do I take it?
Take 2 capsules daily, preferably at the same time each day. Can be taken with or without food, morning or evening.
Do you ship internationally?
Yes we ship worldwide!
Where are your ingredients from?
Ingredients are all-natural, sourced from the US and Europe.
Only 47 bottles left in stock - next restock January 8th

Ready to get 1 poo-gasm every day?
Join 3,200+ women who chose gentle, effective relief over painful straining and constant bloating!